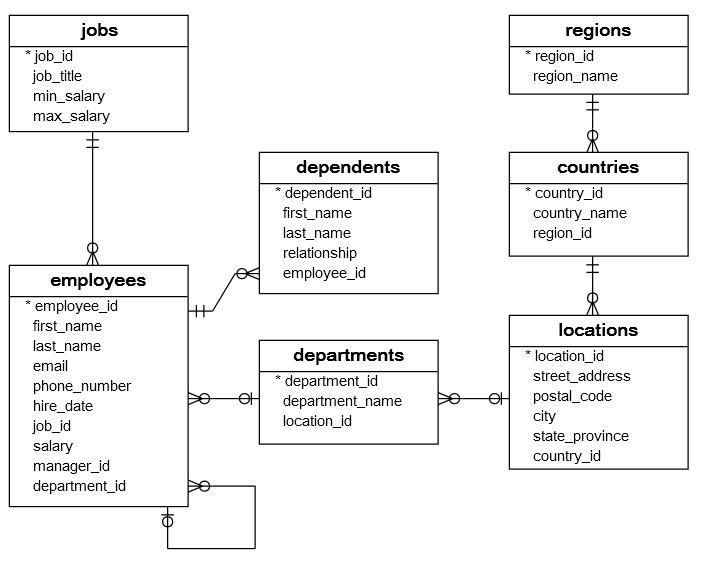
Base de dades de treball: HR. Consultes simples
La revisió el 07:47, 23 nov 2021 per Joan (discussió | contribucions) (Es crea la pàgina amb «=T1. sample database= thunbnail *https://www.sqltutorial.org/sql-sample-database/ =T2: secció 1, 2, 3 i 4 del tutorial= *...».)
T1. sample database
T2: secció 1, 2, 3 i 4 del tutorial
Per executr online els exemples:
Les consultes executades a classe (que són les que hi ha al tutorial que estem seguint), corresponents a aquestes seccions del tutorial:
/*
$ cd /home/joan/DAM_M02_2122/UF2/HR
$ mysql -h localhost -u alumne -pkeiL2lai --verbose HR < ./apunts_sqltutorial.sql > sortida.txt
Section 1: Introduction to SQL
================================
https://www.sqltutorial.org/what-is-sql/
What is SQL – give you a brief overview of the SQL language and its popular dialects.
SQL Syntax – provide you with the syntax of the SQL language.
SQL Sample Database – introduce you to an HR sample database.
*/
/*
Section 2: Querying Data
=================================
https://www.sqltutorial.org/sql-select/
SELECT Statement – show you how to query data from a single table by using the simplest form of the SELECT statement.
*/
/*
SELECT
select_list
FROM
table_name;
SELECT * FROM table_name;
*/
/*
Besides the SELECT and FROM clauses, the SELECT statement can contain many other clauses such as
WHERE – for filtering data based on a specified condition.
ORDER BY – for sorting the result set.
LIMIT – for limiting rows returned.
JOIN – for querying data from multiple related tables.
GROUP BY – for grouping data based on one or more columns.
HAVING – for filtering groups.
*/
SELECT * FROM employees;
SELECT
employee_id,
first_name,
last_name,
hire_date
FROM
employees;
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, hire_date FROM employees;
# diferències entre MySQL, SQL Server, SQLite:
SELECT
employee_id,
first_name,
last_name,
FLOOR(DATEDIFF('2021-01-01', hire_date) / 365) YoS
FROM
employees;
/*
Section 3: Sorting Data
================================
https://www.sqltutorial.org/sql-order-by/
ORDER BY Clause – sort the data by one or more columns in the ascending and/or descending order.
*/
/*
SELECT
column1, column2
FROM
table_name
ORDER BY column1 ASC ,
column2 DESC;
*/
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, hire_date, salary
FROM employees
ORDER BY first_name;
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, hire_date, salary
FROM employees
ORDER BY salary DESC;
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, hire_date, salary
FROM employees
ORDER BY hire_date;
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, hire_date, salary
FROM employees
ORDER BY hire_date DESC;
/*
Section 4: Filtering Data
================================
https://www.sqltutorial.org/sql-distinct/
DISTINCT – show you how to remove duplicates from the result set.
LIMIT – constrain a number of rows returned by a query using the LIMIT and OFFSET clause.
FETCH – learn how to skip N rows in a result set before starting to return any rows.
WHERE Clause – filter data based on specified conditions.
Comparison operators – learn how to use the comparison operators including greater than, greater than or equal, less than, less than or equal, equal, and not equal to form the condition in the WHERE clause.
Logical operators – introduce the logical operators and how to use them to test for the truth of a condition.
AND operator – combine multiple Boolean expressions using the AND logical operator.
OR operator – show you how to use another logical operator OR to combine multiple Boolean expressions.
BETWEEN Operator – guide you to use the BETWEEN operator to select data within a range of values.
IN Operator – show you how to use the IN operator to check whether a value is in the list of values.
LIKE Operator – query data based on a specified pattern.
IS NULL Operator – introduce the NULL concepts and show you how to check whether an expression is NULL or not.
NOT operator – show you how to negate a Boolean expression by using the NOT operator.
*/
/*
SELECT DISTINCT
column1, column2, ...
FROM
table1;
*/
SELECT salary
FROM employees
ORDER BY salary DESC;
SELECT DISTINCT salary
FROM employees
ORDER BY salary DESC;
SELECT job_id, salary
FROM employees
ORDER BY job_id, salary DESC;
SELECT DISTINCT job_id, salary
FROM employees
ORDER BY job_id, salary DESC;
# valors nuls
SELECT DISTINCT phone_number
FROM employees;
/*
SELECT
column_list
FROM
table1
ORDER BY column_list
LIMIT row_count OFFSET offset;
*/
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name
FROM employees
ORDER BY first_name;
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name
FROM employees
ORDER BY first_name
LIMIT 5;
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name
FROM employees
ORDER BY first_name
LIMIT 5 OFFSET 3;
# en mysql es pot fer d'una forma més curta:
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name
FROM employees
ORDER BY first_name
LIMIT 3 , 5;
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, salary
FROM employees
ORDER BY salary DESC
LIMIT 5;
# el 2n salari més alt el trobarem de la següent manera:
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, salary
FROM employees
ORDER BY salary DESC
LIMIT 1 OFFSET 1;
SELECT DISTINCT salary
FROM employees
ORDER BY salary DESC
LIMIT 1 , 1;
# per saber qui són les persones que cobren 17000:
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, salary
FROM employees
WHERE salary = 17000;
# podem combinar totes dues. Això són les subqueries (subconsultes):
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, salary
FROM employees
WHERE salary = (SELECT DISTINCT salary FROM employees ORDER BY salary DESC LIMIT 1 , 1);
/*
SELECT
column1, column2, ...
FROM
table
WHERE
condition;
*/
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, salary
FROM employees
WHERE salary > 14000
ORDER BY salary DESC;
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id
FROM employees
WHERE department_id = 5
ORDER BY first_name;
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name
FROM employees
WHERE last_name = 'Chen';
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, hire_date
FROM employees
WHERE hire_date >= '1999-01-01'
ORDER BY hire_date DESC;
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, hire_date
FROM employees
WHERE YEAR (hire_date) = 1999
ORDER BY hire_date DESC;
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name
FROM employees
WHERE last_name = 'Himuro';
# compte amb el NULL que funciona de manera diferent:
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, phone_number
FROM employees
WHERE phone_number = NULL;
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, phone_number
FROM employees
WHERE phone_number IS NULL;
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id
FROM employees
WHERE department_id <> 8
ORDER BY first_name , last_name;
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id
FROM employees
WHERE department_id <> 8 AND department_id <> 10
ORDER BY first_name , last_name;
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, salary
FROM employees
WHERE salary > 10000
ORDER BY salary DESC;
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, salary
FROM employees
WHERE salary > 10000 AND department_id = 8
ORDER BY salary DESC;
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, salary
FROM employees
WHERE salary < 10000
ORDER BY salary DESC;
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, salary
FROM employees
WHERE salary >= 9000
ORDER BY salary;
T3: aplicació BDQuest
Fem una explicació a classe del funcionament de l'aplicació web. Com que és la primera vegada que aquesta aplicació s'utilitza a classe, els alumnes reportaran els problmemes d'usabilitat que segur que hi haurà, i s'intentarà incorporar tots les millores proposades.
creat per Joan Quintana Compte, novembre 2021